npm-check-updates



npm-check-updates upgrades your package.json dependencies to the latest versions, ignoring specified versions.
- maintains existing semantic versioning policies, i.e.
"express": "^4.0.0" to "express": "^5.0.0". - only modifies package.json file. Run
npm install to update your installed packages and package-lock.json.
You may also want to consider npm-check. Similar purpose, different features.
Installation
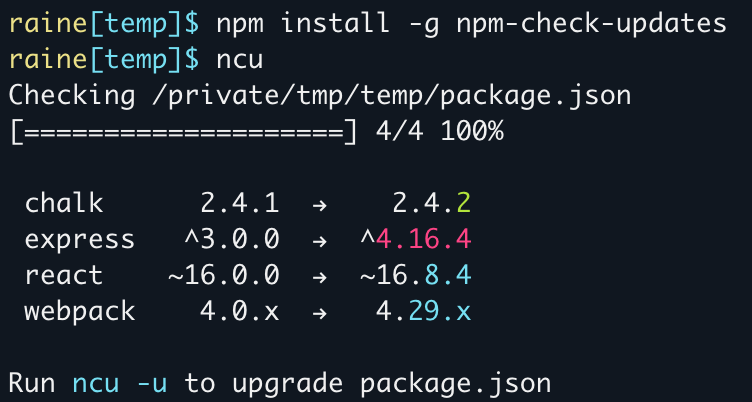
Install globally:
npm install -g npm-check-updates
Or run with npx:
npx npm-check-updates
Usage
Show any new dependencies for the project in the current directory:
$ ncu
Checking package.json
[====================] 5/5 100%
express 4.12.x → 4.13.x
multer ^0.1.8 → ^1.0.1
react-bootstrap ^0.22.6 → ^0.24.0
react-a11y ^0.1.1 → ^0.2.6
webpack ~1.9.10 → ~1.10.5
Run ncu -u to upgrade package.json
Upgrade a project's package file:
Make sure your package file is in version control and all changes have been committed. This will overwrite your package file.
$ ncu -u
Upgrading package.json
[====================] 1/1 100%
express 4.12.x → 4.13.x
Run npm install to install new versions.
$ npm install
Check global packages:
ncu -g
Filter packages using the --filter option or adding additional cli arguments. You can exclude specific packages with the --reject option or prefixing a filter with !. Supports strings, wildcards, globs, comma-or-space-delimited lists, and regular expressions:
ncu mocha
ncu -f mocha
ncu --filter mocha
ncu react-*
ncu "/^react-.*$/"
ncu \!nodemon
ncu -x nodemon
ncu --reject nodemon
ncu chalk mocha react
ncu chalk, mocha, react
ncu -f "chalk mocha react"
ncu \!react-*
ncu '/^(?!react-).*$/'
ncu "/^(?!react-).*$/"
How dependency updates are determined
- Direct dependencies are updated to the latest stable version:
2.0.1 → 2.2.01.2 → 1.30.1.0 → 1.0.1
- Range operators are preserved and the version is updated:
^1.2.0 → ^2.0.01.x → 2.x>0.2.0 → >0.3.0
- "Less than" is replaced with a wildcard:
<2.0.0 → ^3.0.01.0.0 < 2.0.0 → ^3.0.0
- "Any version" is preserved:
- Prerelease and deprecated versions are ignored by default.
- Use
--pre to include prerelease versions (e.g. alpha, beta, build1235) - Use
--deprecated to include deprecated versions
- With
--target minor, only update patch and minor:
- With
--target patch, only update patch:
Options
--color Force color in terminal
--concurrency <n> Max number of concurrent HTTP requests to
registry. (default: 8)
--configFileName <filename> Config file name (default: .ncurc.{json,yml,js})
--configFilePath <path> Directory of .ncurc config file (default:
directory of `packageFile`).
--cwd <path> Working directory in which npm will be executed.
--deep Run recursively in current working directory.
Alias of (--packageFile '**/package.json').
--dep <value> Check one or more sections of dependencies only:
dev, optional, peer, prod, bundle
(comma-delimited).
--deprecated Include deprecated packages.
--doctor Iteratively installs upgrades and runs tests to
identify breaking upgrades. Run "ncu --doctor"
for detailed help. Add "-u" to execute.
--enginesNode Include only packages that satisfy engines.node
as specified in the package file.
-e, --errorLevel <n> Set the error level. 1: exits with error code 0
if no errors occur. 2: exits with error code 0
if no packages need updating (useful for
continuous integration). (default: 1)
-f, --filter <matches> Include only package names matching the given
string, wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited
list, or /regex/.
--filterVersion <matches> Filter on package version using
comma-or-space-delimited list, or /regex/.
--format <value> Enable additional output data, string or
comma-delimited list: ownerChanged, repo.
ownerChanged: shows if the package owner changed
between versions. repo: infers and displays
links to source code repository. (default: [])
-g, --global Check global packages instead of in the current
project.
--greatest DEPRECATED. Renamed to "--target greatest".
-i, --interactive Enable interactive prompts for each dependency;
implies -u unless one of the json options are
set,
-j, --jsonAll Output new package file instead of
human-readable message.
--jsonDeps Like `jsonAll` but only lists `dependencies`,
`devDependencies`, `optionalDependencies`, etc
of the new package data.
--jsonUpgraded Output upgraded dependencies in json.
-l, --loglevel <n> Amount to log: silent, error, minimal, warn,
info, verbose, silly. (default: "warn")
--mergeConfig Merges nested configs with the root config file
for --deep or --packageFile options (default:
false)').
-m, --minimal Do not upgrade newer versions that are already
satisfied by the version range according to
semver.
-n, --newest DEPRECATED. Renamed to "--target newest".
-o, --ownerChanged DEPRECATED. Renamed to "--format ownerChanged".
--packageData <value> Package file data (you can also use stdin).
--packageFile <path|glob> Package file(s) location (default:
./package.json).
-p, --packageManager <name> npm, yarn (default: "npm")
--peer Check peer dependencies of installed packages
and filter updates to compatible versions. Run
"ncu --help --peer" for details.
--pre <n> Include -alpha, -beta, -rc. (default: 0; default
with --newest and --greatest: 1).
--prefix <path> Current working directory of npm.
-r, --registry <url> Third-party npm registry.
-x, --reject <matches> Exclude packages matching the given string,
wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited list,
or /regex/.
--rejectVersion <matches> Exclude package.json versions using
comma-or-space-delimited list, or /regex/.
--removeRange Remove version ranges from the final package
version.
--semverLevel <value> DEPRECATED. Renamed to --target.
-s, --silent Don't output anything (--loglevel silent).
-t, --target <value> Target version to upgrade to: latest, newest,
greatest, minor, patch. Run "ncu --help
--target" for details.` (default: "latest")
--timeout <ms> Global timeout in milliseconds. (default: no
global timeout and 30 seconds per
npm-registery-fetch).
-u, --upgrade Overwrite package file with upgraded versions
instead of just outputting to console.
-V, --version output the version number
-h, --help display help for command
Doctor Mode
Usage: ncu --doctor [-u] [options]
Iteratively installs upgrades and runs tests to identify breaking upgrades. Add -u to execute (modifies your package file, lock file, and node_modules).
To be more precise:
- Runs
npm install and npm test to ensure tests are currently passing. - Runs
ncu -u to optimistically upgrade all dependencies. - If tests pass, hurray!
- If tests fail, restores package file and lock file.
- For each dependency, install upgrade and run tests.
- When the breaking upgrade is found, saves partially upgraded package.json (not including the breaking upgrade) and exits.
Example:
$ ncu --doctor -u
npm install
npm run test
ncu -u
npm install
npm run test
Failing tests found:
/projects/myproject/test.js:13
throw new Error('Test failed!')
^
Now let's identify the culprit, shall we?
Restoring package.json
Restoring package-lock.json
npm install
npm install --no-save react@16.0.0
npm run test
✓ react 15.0.0 → 16.0.0
npm install --no-save react-redux@7.0.0
npm run test
✗ react-redux 6.0.0 → 7.0.0
Saving partially upgraded package.json
Configuration Files
Use a .ncurc.{json,yml,js} file to specify configuration information.
You can specify file name and path using --configFileName and --configFilePath
command line options.
For example, .ncurc.json:
{
"upgrade": true,
"filter": "express",
"reject": [
"@types/estree",
"ts-node"
]
}
Module/Programmatic Usage
npm-check-updates can be required as a module:
const ncu = require('npm-check-updates')
(async () => {
const upgraded = await ncu.run({
packageFile: '../package.json',
upgrade: true,
}))
console.log(upgraded)
})()
Known Issues
- If
ncu prints output that does not seem related to this package, it may be conflicting with another executable such as ncu-weather-cli or Nvidia CUDA. Try using the long name instead: npm-check-updates. - Windows: If npm-check-updates hangs, try setting the package file explicitly:
ncu --packageFile package.json. You can run ncu --loglevel verbose to confirm that it was incorrectly waiting for stdin. See #136.
Problems?
File an issue. Please search existing issues first.







